How to Quote Works Correctly, Following the MLA-8 Format

All college and university students should be aware of the existence of associations such as MLA. They regulate the format of writing scientific papers, which means that from time to time you will refer to their guidelines. At least in order to issue MLA works cited. You won’t learn all the features and nuances by heart, but we have put together a detailed guide for you to help you navigate. Follow our recommendations and visual aids to cite any source with ease and succeed.
Essential Components
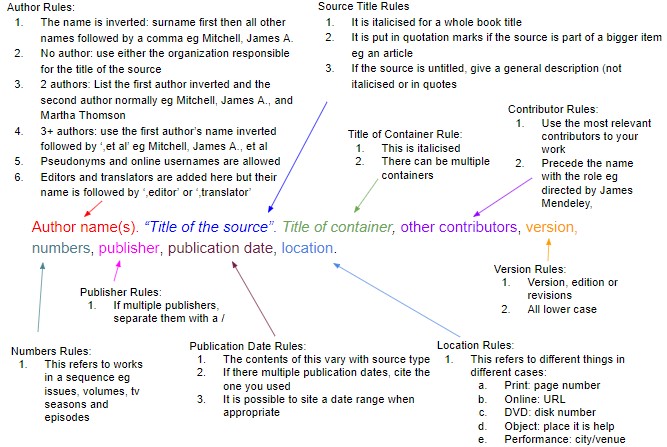
Additionally:
- If you want to add something from yourself that was not mentioned in the original source, add it using square brackets.
- If the date is inaccurate, write “circa” in front of it so that you are correctly understood.
- If some components of the source are doubtful, add “?”
Referencing Basics: MLA works cited-list
If we are talking about the MLA8 format, you need to add a bibliography called the “Works-Cited List”. In this section, you must indicate all the sources that you refer to in your paper. Each source should include title, author’s name, publication date. As well as additional information, depending on its type. Writing the MLA works cited you should:
- Start this from a new page at the very end of the paper.
- Sort it alphabetically. If the names of the authors are known, then starting with the first. If the authors are unknown, then by name.
- Sort several sources of the same author by date, or in alphabetical order if all of them are one year of release.
- Observe double spacing for recordings.
- Use 0.5-inch indentation for the second and subsequent lines of the source.
- If you refer to several works of the same author, in the first link indicate his or her full name, and in subsequent ones replace it with “- – -“.
- For all text links that you use, indicate full links.
Order research paper writing that will also ensure you get an A+ paper.
In-Text Citation
If you used a quote from any other paper or paraphrased it in any way, you will need to include text links. In-Text Citations are quotes that relate to the direct translation of words or to paraphrase them. They have to:
- Correspond to the link indicated in the list of works.
- Contain the first word of the link (this may be the name of the author), as well as the page where it is located.
- Be used immediately after quotes. Brackets or natural pause will do.
For inspiration, use an example by George Noel Gordon Byron:
Byron states “…” (134) Or (Byron 134)
Many Authors
If you refer to a source with 2-3 authors, list their name using the following format:
(Byron, Mitchell and Crimson, 134)
If there are more authors, add “et al” after the name of the first author:
(Byron et al. 189)
No Authors:
If your source does not have an author, you should use the paper title instead. For quotation, highlight italics in quotation marks or quotation marks if it is abbreviations. For example:
Book Title: Citation Guide states “..” (189) Or (Citation Guide 189)
The title of the article: “APA Citation Guide” reads “…” (189) Or (“APA Citation Guide” 189)
There are also different options for the cases when you should cite authors with multiple works, with the same surname, with no page number, etc. In the first case, it would be nice to use a shortened version of the title. In the second case, include an initial: (J. Byron 34) and (A.Byron 123-128). If there is no page number, use chapters and paragraphs instead. (Byron, ch.3). If there are no possible options then quote the name alone.
In case when you need to cite a quote or a parenthetical, use “qtd” before the name of the author (qtd. In Byron 137). You can also cite visual aids, audios or videos, using a timestamp. (Byron 01:34:23)
If you have troubles with write my paper or term papers, contact us!
Different Source Types MLA Works Cited
- If you need to use In-text citation, keep in mind that this depends only on the type of source. What to do in cases where the author is unknown or the audiovisual source we have described in detail above.
- The literature review may vary depending on the source.
Citing Books in MLA Format
Among all the types of references, the most common is book referencing. Here’s what the main format looks like:
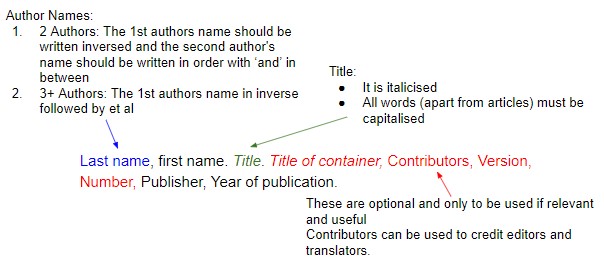
MLA Cited Books: After Edition or Translation
The format of edited and translated books is the same as for book reference. The only exception is that you need to specify the editor or translator of the paper. You have 2 ways to do this:
- Indicate the name after all the names in the list of authors. This is true in case the edited or translated book is at the center of your work. For example, Johnson, Peter, editor.
- Add names to the list of authors, specifying before it “edited” or “translated”. This is necessary in case the focus of your paper is on the author or work, but not the edited version or translation. For example, edited by Peter Johnson.
Here are 2 options available:
- Surname, name, editor. Title. Content title, Authors, Version, Number, Publisher, Year of publication.
- Last name and first name. Title. The name of the content. Authors who edited the paper, version, number, publicist and year of publication.
There are examples of the edited and translated book:

What about E-Books in MLA Format?
Since the e-book fully displays the contents of a regular one, it is considered simply as another version of the book. Therefore, if you need to make a link to an ebook, just add it to other links to books. You also have the opportunity to refer to specific suppliers, such as Amazon Kindle. You can specify “Kindle ed.”
Here is the basic format to follow when quoting an e-book:
Surname and name of the author. Title. The name of the container, List of authors, edition, e-book, number, publisher, year of publication
Take a look at E-Book Example:
![]()
MLA Works Cited: Chapters or Essays
If you need to refer to a chapter in a book or a specific essay, the form will change a little.

Citing articles in MLA Format
Good news, magazines, newspapers, and articles from them are cited in one basic format:
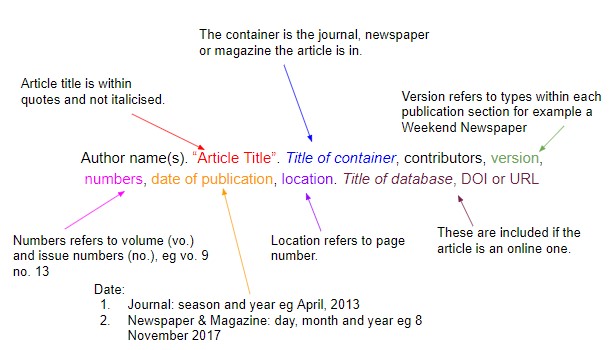
The difference between magazines, newspapers, and articles can only relate to dates and titles of content.
Example with Journal:
Beets, Anthony B. “Nowadays technologies”. Upgrade Journal, vol.7, no.3, Autumn 2003, pp 354-367
Example with Newspaper:
Beets, Anthony B. “Nowadays technologies”. Upgrade, weekend edition. vol.73, no.3, 5 May 2014, pp. 75-84
Online Example:
There is only one change for this type of reference. You should add the database title and don’t forget about URL or DOI where one can find your article.
Beets, Anthony B. “Nowadays technologies”. Upgrade Journal, vol. 3, no. 4, Winter 2003, pp. 574-612. Journal Database. [Link]
Citing Non Print Material
Pictures
If your task is to cite an image, follow the basic format. First things first mention the author’s surname, other names. Then write the title of the picture and the website’s where you’ve found it. Don’t forget about contributors, reproduction. Mention the number and the date. And the URL as well.
An Example to Inspire by:
Saloua Raouda Choucair. “Poem of Nine Verses”. Tate, T13647, 1966-8,
https://www.tate.org.uk/art/artworks/choucair-poem-of-nine-verses-t13647
Citing movie
MLA works cited may be pretty different. And the films are among them.
You should mention:
- the name of the director;
- the title;
- contributors;
- production;
- year of release;
- medium.
If the focus of your paper is different, you can swap the director’s name and the title. Start with the title of the movie, then mention its director and so on.
MLA 8 Guidelines don’t require the medium, but it would be good tone to mention it because it is useful for your readers. If you’ve found the movie online, swap the medium with a URL
For example:
Zemeckis, Robert, director. “Forrest Gump”. Performances by Tom Hanks and Robin Wright, Paramount Pictures, 1994. DVD.
Citing TV Series according to MLA Format
Essentially, referencing TV shows is as easy as referencing movies. The only addition – you need to mention the number of the season and a concrete episode:
- The title of the episode;
- Program Title:
- Created by writers and directors name$
- Contributors;
- Number of the season;
- Number of an episode;
- Network;
- Year of Publication.
Take a look at a good example:
“The Bracket”. How I Met Your Mother, written by Joe Kelly, directed by Pamela Fryman, season 3, episode 14, 2008.
Citing Music
Don’t limit yourself to quoting movies and TV shows. If you refer to your favorite or important music for your research, indicate this. There is a basic structure:
- Author name or names;
- Track title;
- Album title;
- Contributors;
- Version;
- Record Label;
- Year of Publication.
Please take a look at an example:
Britney Spears. “Oops, I did it again”, Oops, I did it again, Cheiron Studios, Battery Studios, 2000.
How to Cite a Webpage According to MLA Format
You can also refer to different websites. Consider what you should mention. The surname of the author, his or her first name. Then the title of the particular document or page, italicized title of the website. Finish with the date and URL.
Not all students can immediately understand all the nuances of citation. You have to constantly contact your mentor, open a guide, and study the features. Most likely you will make some mistakes. Therefore, carefully reread your paper to make sure that it is written correctly and professionally. Or entrust its preparation to experienced writers who are familiar with all the nuances of MLA8. We guarantee you a quality result on time.

 Calculate
Calculate